What is E-Commerce and How to Maximize Profits in E-Commerce: A Complete Guide
E-commerce, short for electronic commerce, has revolutionized the way businesses operate and consumers shop. It offers a convenient and efficient platform for buying and selling goods and services online. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what e-commerce is, the different types of e-commerce models, and strategies to maximize profits in this dynamic industry.
Table of Contents
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- Business-to-Business (B2B)
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
- Choosing a Niche and Products
- Setting Up Your Online Store
- Payment Gateways and Security
- Logistics and Fulfillment
- Optimizing Your Website
- Effective Marketing Strategies
- Customer Retention and Loyalty Programs
- Expanding Product Range and Upselling
1. Understanding E-Commerce
E-commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet. It encompasses a wide range of business models, including retail, wholesale, dropshipping, and digital products. E-commerce platforms allow businesses to reach a global audience, operate 24/7, and provide convenient shopping experiences for customers.
2. Types of E-Commerce Models
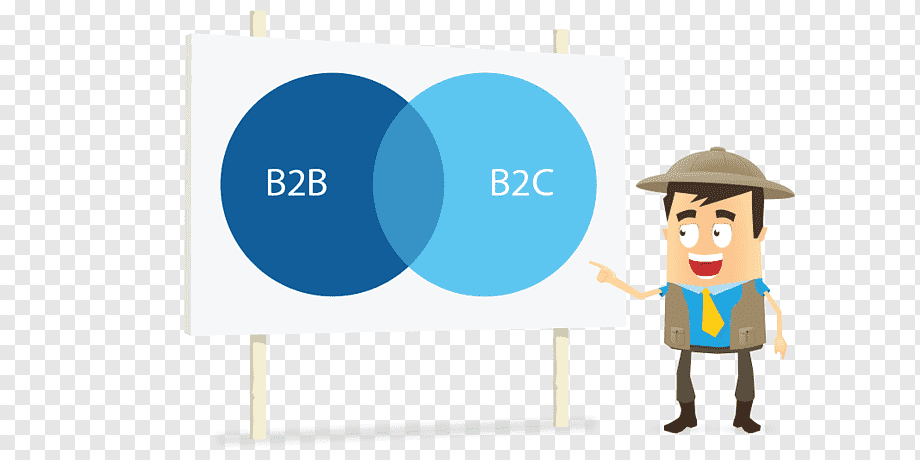
2.1 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
B2C is the most common e-commerce model where businesses sell products directly to consumers. Examples include online retailers like Amazon, clothing stores, and electronic shops. The B2C model focuses on providing a seamless shopping experience and customer service.
2.2 Business-to-Business (B2B)
In the B2B model, businesses sell products or services to other businesses. This model is prevalent in industries like manufacturing, wholesale, and software. B2B transactions often involve larger order volumes and longer sales cycles compared to B2C.
2.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
C2C e-commerce platforms facilitate transactions between consumers. Websites like eBay and Craigslist are examples where individuals can buy and sell products to one another. These platforms act as intermediaries, providing a marketplace for users.
2.4 Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
In the C2B model, individuals offer products or services to businesses. This can include freelance work, influencer marketing, and user-generated content. Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr are examples where consumers offer services to businesses.
3. Benefits of E-Commerce
E-commerce offers numerous advantages for both businesses and consumers:
- Global Reach: Businesses can reach customers worldwide, breaking geographical barriers.
- Lower Operating Costs: E-commerce reduces the need for physical storefronts, lowering overhead costs.
- Convenience: Customers can shop anytime, anywhere, and have access to a wide range of products.
- Data Insights: E-commerce platforms provide valuable data on customer behavior, allowing businesses to tailor their offerings.
4. How to Start an E-Commerce Business
4.1 Choosing a Niche and Products
The first step in starting an e-commerce business is choosing a niche and products to sell. Research market trends, customer demand, and competition. Focus on a niche that aligns with your interests and expertise. Consider factors like product profitability, sourcing, and shipping logistics.
4.2 Setting Up Your Online Store
Select an e-commerce platform to build your online store. Popular platforms include Shopify, WooCommerce, and BigCommerce. Customize your store’s design, layout, and branding to create a professional and user-friendly experience. Ensure your website is mobile-responsive, as a significant portion of online shopping is done on mobile devices.
4.3 Payment Gateways and Security
Choose a reliable payment gateway to process transactions securely. Options include PayPal, Stripe, and Square. Implement SSL certificates and other security measures to protect customer data and build trust. Make the checkout process simple and efficient to reduce cart abandonment.
4.4 Logistics and Fulfillment
Decide how you will handle shipping and fulfillment. Options include self-fulfillment, third-party logistics (3PL), and dropshipping. Consider factors like shipping costs, delivery times, and inventory management. Offer multiple shipping options and transparent delivery estimates.
5. Strategies to Increase E-Commerce Profits

5.1 Optimizing Your Website
A well-optimized website can significantly impact your e-commerce profits. Improve your website’s loading speed, ensure easy navigation, and create clear calls to action. Optimize product pages with high-quality images, detailed descriptions, and customer reviews. Implement SEO best practices to improve search engine rankings and drive organic traffic.
5.2 Effective Marketing Strategies
Utilize various marketing strategies to drive traffic and increase sales. This includes content marketing, social media advertising, email marketing, and pay-per-click (PPC) advertising. Leverage platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and Instagram Shopping. Track the performance of your campaigns and adjust strategies based on data insights.
5.3 Customer Retention and Loyalty Programs
Retaining existing customers is more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. Implement loyalty programs, offer discounts, and provide excellent customer service to encourage repeat purchases. Collect customer feedback and continuously improve your products and services. Personalized marketing and exclusive offers can also enhance customer loyalty.
5.4 Expanding Product Range and Upselling
Expand your product range to cater to a broader audience and increase your average order value. Analyze customer preferences and market trends to introduce new products. Upselling and cross-selling techniques can also boost your profits. Recommend complementary products or higher-end alternatives to customers during the shopping process.
6. Scaling Your E-Commerce Business
6.1 Automation and Efficiency
As your e-commerce business grows, automation becomes crucial for efficiency. Use tools and software to automate tasks like inventory management, order processing, and email marketing. This saves time and reduces the risk of human error. Streamlining operations allows you to focus on strategic growth and customer experience.
6.2 International Expansion
Expanding into international markets can significantly increase your customer base and revenue. Research and understand the regulations, taxes, and cultural differences in each target market. Offer multi-currency payment options and localized content to cater to international customers. Use global marketplaces like Amazon and eBay to reach international audiences.
7. Common Challenges in E-Commerce and Solutions
E-commerce businesses face challenges like competition, cyber threats, and changing market trends. To overcome these challenges, stay updated with industry trends, invest in cybersecurity, and continuously innovate your products and services. Build a strong brand presence and maintain excellent customer relationships to differentiate yourself from competitors.
8. Conclusion
E-commerce offers immense opportunities for entrepreneurs and businesses to reach a global audience and maximize profits. By understanding the fundamentals of e-commerce, choosing the right business model, and implementing effective strategies, you can build a successful e-commerce business. Stay adaptable, embrace new technologies, and focus on delivering value to your customers to thrive in the ever-evolving world of e-commerce.